Phiala Thouvenin, Ph.D.'s Portfolio
Coding Projects and Examples
Calculating wedge slopes
- Take output from surface_generator
- Extract the section of the wedge before the deformation front
- Sample this extracted topography and fit a slope using least squares.
- All measurements are in pixels
Module imports
import pims
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from utils import *
## pjt_slope15_prebuilt_062218, high fric baseline parameters
images = pims.ImageSequence('data/*.jpg')
xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax = 95, 5095,300, 1290 # pixel boundaries of image crop
scale=63. #pixels/cm spatial
im_w=images.frame_shape[1]
im_h=images.frame_shape[0]
surfs = 'pjt_slope15_prebuilt_062218_surfnocv_2023.h5'
Examine wedge surfaces
surf = pd.read_hdf(surfs,'wedgetop_00000')
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
plt.imshow(images[0][ymin:ymax,xmin:xmax])
plt.plot(surf.x-xmin,-surf.y+im_h-ymin,'k--')
plt.legend(['Surface'])
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f6f8e7d3d00>

Calculate deformation front position
- Use image processing tools to identify curvature in the surface of each wedge
- Identify deformation front as the very front of deformed topography.
- This position changes throughout each experiment.
def deformation_front_mode(surfs,xmin,ymax,im_h,far_edge_count=1000,
threshold=10,
from_larger=True, vergence='s'):
'''
Examine calcuated surfaces, and determine the surface expression of their
deformation fronts over the length of an experiment.
Perform calcuation on surface with the retrowedge as the first area that
exceeds the average flat topography elevation, and the deformation
front defined as the last area that exceeds elevation outside of
a specifed range of [sand_elev +/- surfvar].
Calcuated value is only the physical expression of the deformation front,
as actual deformation may jump forelandward for a short time
before surface expression.
'''
surfs_keys = list(h5py.File(surfs,'r'))
# determine maxlimum width of profile
len_x = []
for i, key in enumerate(surfs_keys):
surf = pd.read_hdf(surfs,key)
if from_larger:
surf.x = surf.x - xmin
surf.y = surf.y - (im_h-ymax)
len_x.append(surf.x.max())
width = int(max(len_x))
# place surface in preallocated array
surface = np.zeros((len(surfs_keys),width))
for i, key in enumerate(surfs_keys):
surf = pd.read_hdf(surfs,key)
surf = surf.y.dropna().reindex(surf.x, method='nearest').reset_index()
if from_larger:
surf.x = surf.x - xmin
surf.y = surf.y - (im_h-ymax)
surface[i,np.array(surf.x.values,dtype='int')-1] = surf.y.values
# determine mean height of foreland material on far edge of surface array
far_edge_mean = surface[:,-far_edge_count:].mean()
# mask to find area that is within a given elevation of this mean
mask = (surface > far_edge_mean - threshold) & \
(surface < far_edge_mean + threshold)
# set boolean mask on edges to remove edge effects
mask[:,-far_edge_count:] = True
# different modes for either style of model
if vergence == 's':
edge = nd.filters.sobel(mask.astype(float))
front = []
for i in range(edge.shape[0]):
if len(edge[i,:][edge[i,:] > 0]):
front_loc = np.nonzero(edge[i,:])[0][-1]
front.append([i,front_loc])
else:
front.append([i,np.nan])
front = pd.DataFrame(front,columns=('frame','x_df'))
if vergence == 'd':
mask[:,:far_edge_count] = True
edge = nd.filters.sobel(mask.astype(float))
front = []
for i in range(edge.shape[0]):
if len(edge[i,:][edge[i,:] > 0]):
retro_loc = np.nonzero(edge[i,:])[0][0]
front_loc = np.nonzero(edge[i,:])[0][-1]
front.append([i,retro_loc,front_loc])
else:
front.append([i,np.nan,np.nan])
front = pd.DataFrame(front,columns=('frame','x_rf','x_df'))
elif vergence != 's' and vergence != 'd':
raise ValueError('Choose either singly (s) or doubly (d) vergent mode')
return front
front = deformation_front_mode(surfs,xmin,ymax,im_h)
front
| frame | x_df | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3795 |
| 1 | 1 | 3795 |
| 2 | 2 | 3795 |
| 3 | 3 | 3792 |
| 4 | 4 | 3789 |
| 5 | 5 | 3786 |
| 6 | 6 | 3783 |
| 7 | 7 | 3780 |
| 8 | 8 | 3782 |
| 9 | 9 | 3782 |
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
plt.imshow(images[0][ymin:ymax,xmin:xmax])
plt.plot(surf.x-xmin,-surf.y+im_h-ymin,'k--')
plt.vlines(front.iloc[0].x_df+xmin,0,ymax-ymin)
plt.ylim(ymax-ymin,0)
plt.legend(['Surface','Deformation Front'])
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f6f8b70f310>

Fit surface of wedge
- Here we are demarcating the wedge as any material between the backstop (i.e., x=0) and the deformation front.
- The defintition of the active wedge is changable, and others may define the wedge as the material between the first interruption in topography (~1000 pixels across the image) and the deformation front.
def slope_deffront(surfs,front,window=81,peak_thres=0.4,
scale=70.,plotting=False,sgol=False):
'''
FOR SINGLY-VERGENT WEDGES ONLY
Examine calcuated surfaces, and determine the surface expression of their
deformation fronts over the length of an experiment.
Perform calcuation on Gaussian-filtered surface, as raw surface is noisy
enough to interfere with properly identifying the deformation front,
as the last "turn" in the surface, topography decreasing to the left.
Calcuated value may NOT be actual deformation front, as deformation may
jump forelandward for a short time before surface expression.
THEN, calcuate the slope of the surface BEFORE the deformation front,
TODO:
- modify to calcuate last peak of curvature, to detect the retrowedge
boundary in doubly-vergent analog models, and calcuate both
pro- and retro-wedge slopes
'''
slope = []
surfs_keys = list(h5py.File(surfs,'r'))
for i, key in enumerate(surfs_keys):
# read each surface
surf = pd.read_hdf(surfs,key)
surf = surf.y.dropna().reindex(surf.x, method='nearest').reset_index()
# calcuate slope of topography BEFORE the deformation front [fronts]
max_surf = surf[surf.y == surf.y.max()].index.values[0]
if len(surf[(surf.x <= surf.x[front.iloc[i].x_df]) & (surf.x >= surf.x[max_surf])]) >= 3:
wedge_topo = surf[(surf.x <= surf.x[front.iloc[i].x_df]) & (surf.x >= surf.x[max_surf])]
else:
wedge_topo = surf[(surf.x <= surf.x[front.iloc[i].x_df])]
m,b = line_fit(wedge_topo.x,wedge_topo.y)
slope.append(m)
if plotting:
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
fitline = wedge_topo.x * m + b
plt.plot(surf.x,surf.y,'k+',wedge_topo.x,fitline,'r-');
plt.text(3000,800,f'Slope is {abs(m*180/np.pi)}{chr(176)}')
plt.axis('scaled')
plt.ylim([0,1000])
plt.xlabel('Width')
plt.ylabel('Height')
plt.title(f'Slope Fit For Surface: {key}')
plt.savefig(f'fit_surf_{key}.png',bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close('all')
return slope
slopes = slope_deffront(surfs,front,plotting=True)
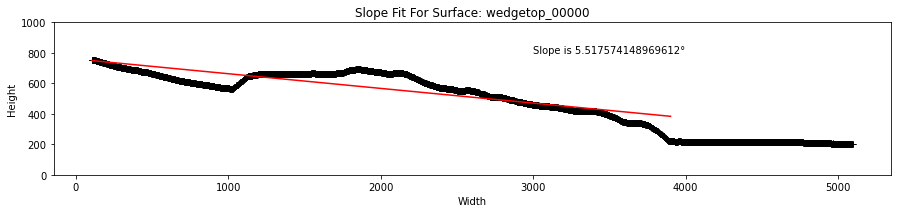
- Here we see that the average slope of the wedge is roughly 5.5 degrees from horizontal.